Exclusivity Pattern
Pattern Overview
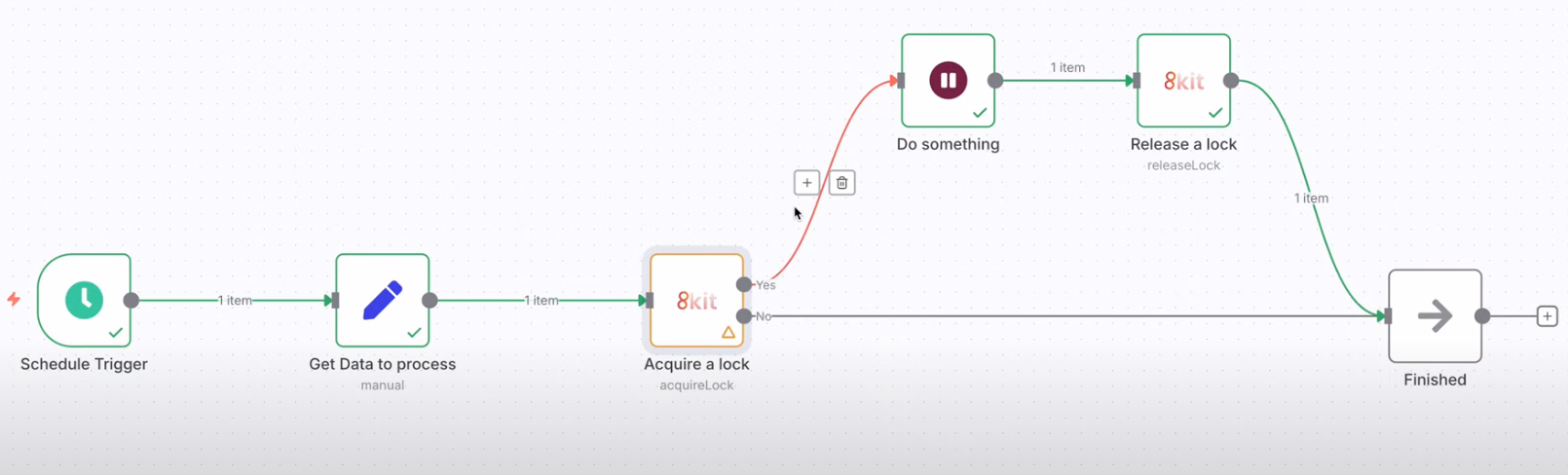
The Exclusivity Pattern uses 8kit's Locks functionality to coordinate n8n workflow executions, preventing race conditions and ensuring only one n8n workflow execution can access a resource at a time.
How It Works
Resource Access → Acquire Lock → Success? → Yes → Perform Operations → Release Lock
↓
No → Wait/Retry → Handle Failure
Key Benefits
- Prevents race conditions - Only one workflow can access resources at a time
- Ensures data integrity - Critical operations are protected from interference
- Coordinates workflows - Multiple workflows can safely share resources
- Handles failures gracefully - Timeout and retry mechanisms built-in
Video Demonstration
What is the Exclusivity Pattern?
The Exclusivity Pattern uses 8kit's Locks to implement distributed locking mechanisms for n8n workflows. It ensures that:
- Only one n8n workflow execution can access a shared resource at a time
- Race conditions are prevented between n8n workflow executions
- Critical sections are protected in n8n workflows
- Resource conflicts are avoided in n8n automation
Key Concepts
- Lock: A mechanism to control access to shared resources in n8n workflows
- Acquire Lock: Request exclusive access to a resource for n8n workflow execution
- Release Lock: Free the resource for other n8n workflow executions
- Lock Timeout: Automatic release after a specified time
- Deadlock Prevention: Avoid infinite waiting scenarios in n8n workflows
When to Use the Exclusivity Pattern
Use the Exclusivity Pattern when you need to:
- Prevent race conditions between n8n workflow executions
- Coordinate file processing across multiple n8n workflows
- Limit API rate across multiple n8n workflow executions
- Ensure atomic operations on shared resources in n8n workflows
- Handle resource conflicts gracefully in n8n automation
Common Use Cases
- File Processing: Ensure only one n8n workflow execution processes a file
- API Rate Limiting: Coordinate API calls across multiple n8n workflow executions
- Database Operations: Prevent concurrent modifications in n8n workflows
- Resource Allocation: Manage limited resources in n8n automation
- Batch Processing: Coordinate large-scale operations in n8n workflows
Implementation Process
The Exclusivity Pattern ensures safe access to shared resources through a systematic locking approach:
Step 1: Acquire a Lock
Before accessing a shared resource, attempt to acquire exclusive access:
- Identify the resource - Determine what needs to be protected (file, database record, API endpoint)
- Request exclusive access - Try to acquire a lock for the specific resource
- Set appropriate timeout - Define how long to wait for the lock
- Handle acquisition result - Proceed if successful, handle failure if not
Step 2: Perform Critical Operations
Once you have exclusive access to the resource:
- Execute protected operations - Perform the critical work that needs coordination
- Maintain lock ownership - Keep the lock active during the entire operation
- Handle errors gracefully - Ensure locks are released even if operations fail
- Validate results - Confirm the operations completed successfully
Step 3: Release the Lock
After completing the critical operations:
- Release exclusive access - Free the lock for other processes
- Clean up resources - Ensure all temporary states are cleared
- Log the completion - Record successful lock usage for monitoring
- Handle cleanup errors - Plan for cases where lock release fails
Key Principles
- Always acquire first - Never access shared resources without coordination
- Release promptly - Free locks as soon as operations complete
- Handle failures - Plan for lock acquisition failures and timeouts
- Use appropriate timeouts - Set reasonable wait times for lock acquisition
- Monitor lock usage - Track lock performance and identify bottlenecks
- Options include:
- Wait and retry
- Skip processing
- Queue for later processing
Screenshot: Complete Exclusivity Pattern - Full workflow with all components connected
Next Steps
Now that you understand the Exclusivity Pattern:
- Try the Temporal Pattern for incremental polling
- Combine patterns for complex scenarios
- Explore advanced techniques for your specific use case
Ready to implement? Start with a simple file processing scenario and gradually add complexity as you become more comfortable with the pattern.